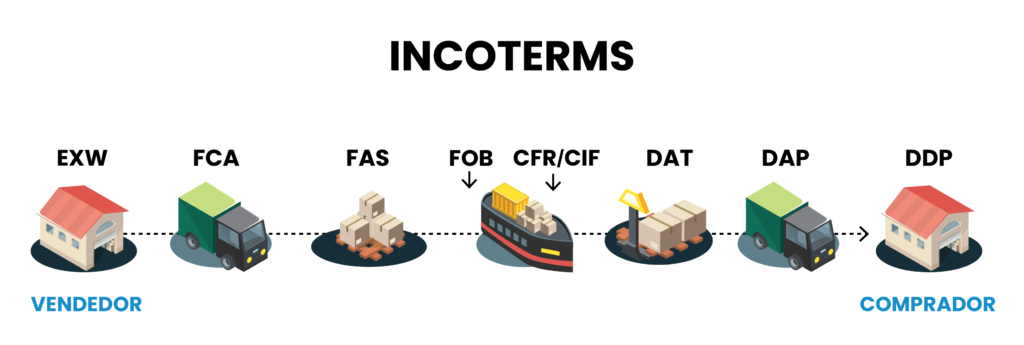
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) are a set of predefined terms by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that are used in international sales contracts. These terms clearly establish the obligations of buyers and sellers regarding transportation, risks, and costs in international trade.
There are several types of Incoterms, including EXW (Ex Works), FCA (Free Carrier), FAS (Free Alongside Ship), FOB (Free on Board), CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), CFR (Cost and Freight), DAT (Delivered at Terminal), DAP (Delivered at Place), and DDP (Delivered Duty Paid). Of these, Incoterms EXW, FOB, CIF and DDP . Among these, at Condensa, the Incoterms we use most frequently are EXW, FOB, CIF, and DDP, as they best meet the needs and preferences of our clients in their commercial transactions.
EXW (Ex Works)
The EXW term is one of the simplest, where the seller makes the goods available at their premises or another agreed location. From that point on, the buyer assumes all costs and risks related to transportation, including export, insurance, and customs clearance. This Incoterm is often chosen by buyers who have experience in managing international logistics and want full control over the shipping process. However, it requires the buyer to handle all aspects of transportation and customs clearance, which can be challenging without proper expertise.
FOB (Free on Board)
FOB is one of the most widely used Incoterms in international shipping, particularly in maritime trade. Under the FOB term, the seller is responsible for delivering the goods on board the vessel at the designated port of shipment. Once the goods are loaded onto the ship, the responsibility transfers to the buyer. This Incoterm is ideal for buyers who prefer control over the shipping process once the goods are on board, allowing them to choose their own carriers and manage the freight costs and insurance according to their needs.
CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight)
CIF is commonly used in shipping, where the seller covers transportation and insurance costs until the goods arrive at the port of destination. The buyer, however, assumes the responsibility as soon as the goods are shipped. This term is ideal for buyers who prefer to limit their involvement in the initial logistics and want the security of having insurance coverage provided by the seller. Buyers should be aware that although the seller manages the initial transport, they must take over once the goods are on board the ship.
DDP (Delivered Duty Paid)
DDP is the Incoterm in which the seller assumes maximum responsibility for delivering the goods. Under this agreement, the seller is responsible for all costs and risks until the goods are delivered to the place designated by the buyer, including the payment of duties, taxes, and customs duties. This makes DDP an extremely favorable term for buyers who want a hassle-free transaction, as they are relieved of virtually all logistical and customs responsibilities. It is particularly beneficial for buyers who prefer not to deal with the complexities of international shipping and customs procedures.
Understanding Incoterms is crucial for successful international trade. Whether you’re a seasoned importer or new to global markets, choosing the right Incoterm can significantly impact your costs, risks, and overall control of the transaction.
We encourage you to explore all your options and make an informed shipping decision that best suits your business needs. At Condensa, we are committed to guiding and supporting our clients through the complexities of global trade.